
Spin forming principle-CNC metal spinning technology
What is CNC metal spinning
CNC metal spinning (Computer Numerical control) is an advanced metal forming technology developed on the basis of manual spinning. This technology combines traditional spinning with modern numerical control technology. It is widely used in the production of rotary parts in fields such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, lighting and kitchenware.
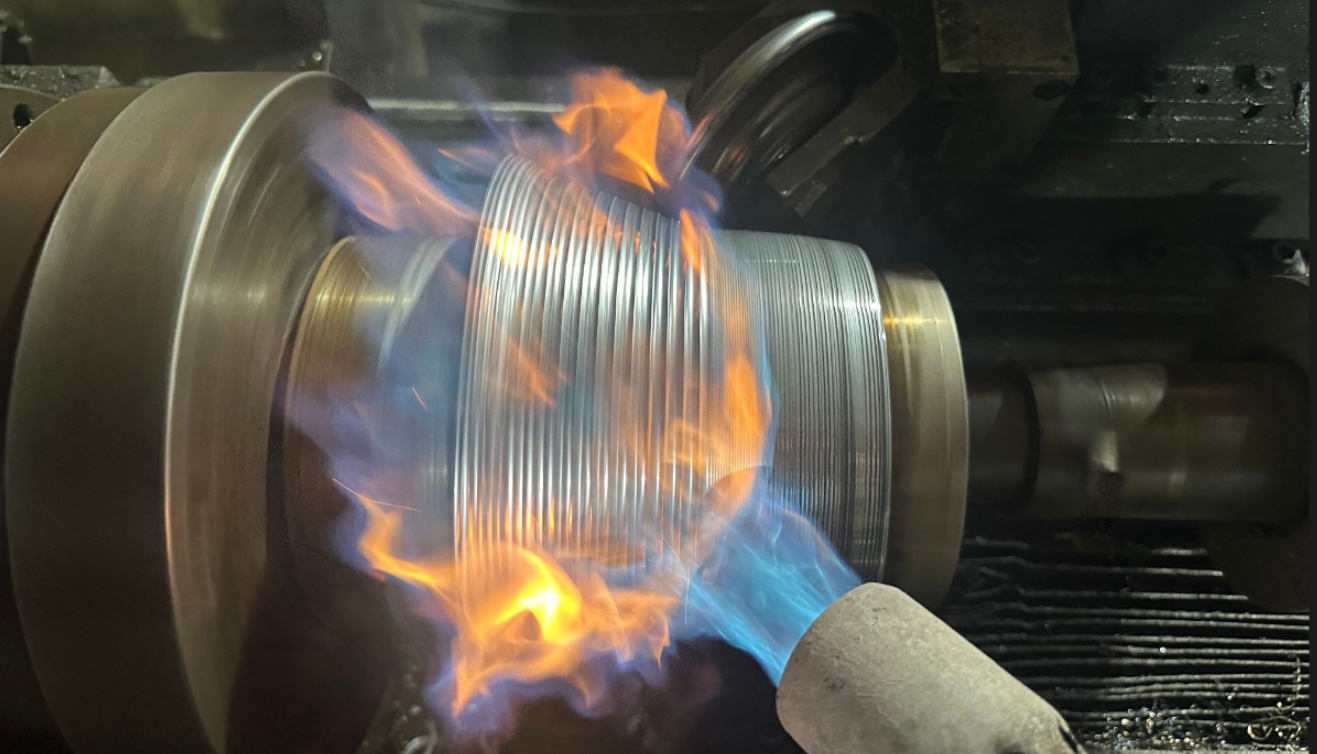

The advantage of CNC metal spinning
CNC spinning greatly reduces the labor force required for manual spinning, achieving higher production efficiency and precision, and having a wider range of metal processing capabilities. However, due to the limitations of human strength, manual spinning can generally only spin stainless steel with a thickness of less than 1mm, aluminum with a thickness of less than 2mm, and iron with a thickness of less than 1.2mm. By designing the power of the servo motor and the reduction ratio of the pulley or reducer reasonably, numerical control spinning can be used to spin thicker and harder metals.
Manual spinning marketing
Manual spinning mainly targets markets such as lighting fixture shells, stainless steel and aluminum tableware, and electrical appliance protective shells. These accessories are all static parts and do not have high requirements for mechanical properties.

CNC metal spinning marketing
CNC metal spinning is applied to automotive wheel hubs, shock absorber housings, pulleys, aerospace parts, Most of these parts have requirements for mechanical properties, such as material hardness, tensile strength, and the weight of the parts. All of these belong to dynamic components that have high requirements for movement. Thanks to the powerful spinning force of CNC spinning, the material undergoes not only tensile deformation but also shear deformation during the forming process, while manual spinning only has shear deformation. Therefore, the grains of parts formed by CNC spinning are thinner, and when forming the same wall thickness and shape, the structural strength is better than that formed by manual spinning.

Future development trend
In the past 20 years, CNC metal spinning has gradually and comprehensively replaced manual spinning. In addition to the processing capacity, production efficiency and processing accuracy of CNC spinning being superior to those of manual spinning. The most important thing is that the CNC spinning machine can be perfectly connected with mechanical automation equipment to achieve fully automated unmanned production. At present, many equipment manufacturers have developed automatic programming software. All you need to do is draw the tool path and input it into the software to obtain the corresponding numerical control program. Although some companies are gradually developing tool paths for automatic drawing and spinning forming, the current technology is not yet very mature. With the development of AI intelligence, the programming and tool path drawing of CNC spinning machines will also be replaced by software and AI algorithms in the future.

Is it easy to learn CNC spinning
For those who are new to the CNC spinning industry or previously engaged in the manual spinning industry, they do not know how to learn CNC spinning technology. In fact, learning numerical control spinning technology is not difficult. Generally, it takes one year to learn the basic knowledge of metal spinning, you can independently analyze and draw the spinning path to complete the forming of different metals and shapes.
CNC metal spinning technology
1. Mandrel and roller design
Different shapes of spun products require different spinning mandrel (it is also called mold ) and roller.
The mandrel design> for spinning is relatively simple. The shape curves of the mandrel for conventional spinning and shear spinning are the internal curves of the spun products. For the necking and tube spinning, molds or fixtures need to be designed to hold the outer diameter part of the product, the gap should be controlled within 0.5mm as much as possible.
The spinning roller design> mainly takes into account the R value and diameter of the roller. Inside the cutter wheel, a pair of tapered roller bearings are installed. It can withstand both axial and radial forces simultaneously.
2. The hardness of roller and mandrel
The roller and the mold need hardness to withstand the wear caused by the friction of the workpiece during the spin forming process. The harder the metal to spin, the harder hardness of the spinning mold and the roller needs to be.
Generally, 45 # steel can be used as the material for spinning aluminum molds, 40CR mold for spinning steel, and Cr12mov mold for spinning stainless steel or materials harder than stainless steel.
The material for the spinning roller can be Cr12mov and DC53. Although high-speed steel has a relatively high hardness, due to its poor toughness, the roller is prone to cracking during spinning at high temperatures and extrusion.
Generally, the molds used for manual spinning are made of 45 # steel. Due to the limitation of human resources, manual spinning only has conventional spinning and does not form shearing spinning. Therefore, the molds for manual spinning do not need to be very hard. However, the hardness and precision of the molds for CNC spinning need to be better than those for manual spinning.
3. Analysis of the spinning performance of materials
Metal spinning can form different metal materials, such as Aluminum, Steel, Stainless steel, red Copper, Brass, Nickel, Titanium, High-temperature alloys, and Inconel. In the analysis of the spinning performance of metals, the three parameters of tensile strength, hardness, and ductility mainly affect the spinning performance. The metal has greater tensile strength, the springback is bigger after spinning. The metal with harder hardness needs stronger spinning force. If the metal has worse the ductility, the depth of the spinning forming is shallower.
If you encounter a material that has never been spun before, you can compare its tensile strength, hardness and ductility (elongation) with that of stainless steel 304, and then you can roughly determine the spinning performance of this material.
4. The spinning properties of commonly used spinning materials
● Aluminium spinning
Based on the analysis of Dinnovation metal spinng> technical experience in spinning, pure aluminum (1060, 1100, 1070 ) have excellent ductility and it is the best to form. The corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy 3003 is better than that of the 1 series, and the spinning springback is slightly greater than that of the 1 series. Aluminum alloy 5052 has the best tensile strength, but the springback during the spinning process is the greatest. The hardness of aluminum 6061 and 6063 is the highest after aging, and the cold work hardening is also more obvious during the spinning process. Therefore, when spinning 5052 and 6061, the blank can be heated appropriately. Aluminum has a fast thermal conductivity and is usually preheated for about 20 seconds, Heating it appropriately again during the spin forming .
2024 and 7075 are aviation and aerospace materials. The tensile strength of 2024 and 7075 is better than that of 5052, and 7075 has the best tensile strength. Material 7075 can be heated during spinning, if it is heated with high temperature, the 7075 material is prone to brittleness and cracking.
● Copper spinning
Red copper is also known as purple copper. Pure copper (TU1, TU2) like pure aluminum, it is very soft and has good ductility, its spinning performance is similar to that of pure aluminum.The spinning performance of brass H65 and H63 is the best among brass, but the spinning springback of brass is relatively large. It is best to heat it during the spinning process.
● Steel spinning
Steel can be classified into low-carbon high carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel according to its carbon content. Low-carbon steel has the best hardness and ductility, so it is advisable to choose low-carbon steel for spinning as much as possible, such as the commonly used DC01, DC02, DC03, DC04, Q235,Q275,Q345, and SPCC. Among them, DC04 has the best ductility and it is the best material for deep drawing (its ductility is slightly lower than aluminum). Q275 and Q345, due to their relatively high tensile strength, require greater spinning force to form. Their ductility is slightly lower than that of other mild steel, but they are still easier to form than stainless steel 304. SPCC sheets are generally galvanized on the surface. The surface of galvanized sheets will not fall off during the spinning process, and the corrosion resistance of the galvanized layer will not decrease after spinning.
● Stainless steel spinning
Stainless steel is much more difficult to shape than iron because its hardness and tensile strength are both greater than those of iron. Among stainless steels, the one with the best formability is 316, which has the best ductility and corrosion resistance. The second best rolled material is stainless steel 304DDQ. There are many different grades of 304, and you need to purchase DDQ, which is specifically designed for deep drawing applications. The 310 type stainless steel has good heat resistance. Its spinning performance is inferior to that of 304. The 201 type has poor corrosion resistance and relatively high tensile strength and hardness. Among these types of stainless steel, it has the poorest spinning performance.
● Titanium spinning
Pure titanium TA1 and TA2 are the most suitable for spinning among titanium alloys. The tensile strength of titanium is greater than that of stainless steel 304, while its hardness is lower than that of stainless steel 304. Pure titanium has a significant springback when being formed by spinning, and it is difficult to be bent. The edges of the blank are prone to wrinkling during spin forming. Heating the titanium during the spinning process can make it easier to be formed. In addition, titanium is prone to sticking by turning, and the tool particles wear out relatively quickly. It is also advisable to electroplate the surface of the spinning roller to increase its hardness. The hardness and tensile strength of TC4 are higher than those of pure titanium. Therefore, only hot spinning can form TC4.
● High-temperature alloy spinning
Superalloys, also known as superalloys, have greater hardness and tensile strength than SUS304. During hot spinning, the raw materials that need to be heated with propane and make it turn red. Otherwise, the superalloy is prone to cracking due to insufficient ductility, or the workpiece does not adhere to the mold, resulting in uncontrollable dimensional accuracy.
● Inconel alloy spinning
The most commonly used Inconel alloys are 718 and 625. This material is mainly used in aircraft tail jet or nozzle positions of turbine engines. It needs to be heated to 300-400 degrees Celsius in spin forming, and there is no need to turn the material red by heating.
The spin forming performance and the application of various materials>
5. Thinning rate
● The principle of thinning
The blank is extruded by the spinning roller, it will become thinner. There are two ways for the blank to become thinner during the deformation process. The first is the stretching thinning after the workpiece is pulled by the roller. The second thinning is caused by the 45º shearing deformation when the roller press the workpiece on the mold.
● Factors affecting the thinning rate
The thinning rate of spinning is related to the radius and quantity of the roller, spin forming path, the spindle speed and the feed speed. The radius of the roller is bigger, the number of the roller is more, the spindle speed is higher, the feed speed is slower, final spinning product is thinner.
● Evaluate the spinning thinning rate
The thinning rate is rather difficult for beginners to estimate. You can cut the spun products of different shapes, conduct thickness tests on them, and compare the final formed thickness with the thickness of the raw material. After comparing and analyzing about 20 to 30 products, you will have a good grasp of the thinning rate.
6. Blank calculation
When we know how to estimate the thinning rate of metal spinning, we can estimate the diameter and thickness of the blank sheet.
Estimation of the blank diameter or thickness of spin forming>
7. Spin forming path drawing
The drawing of spin forming path is the most challenging part in CNC metal spinning technology. It requires an analysis of the spinning characteristics of the material and the shape and structure of the spun metal product, and the selection of the appropriate R value and number of spinning roller to draw the correct and reasonable forming path.
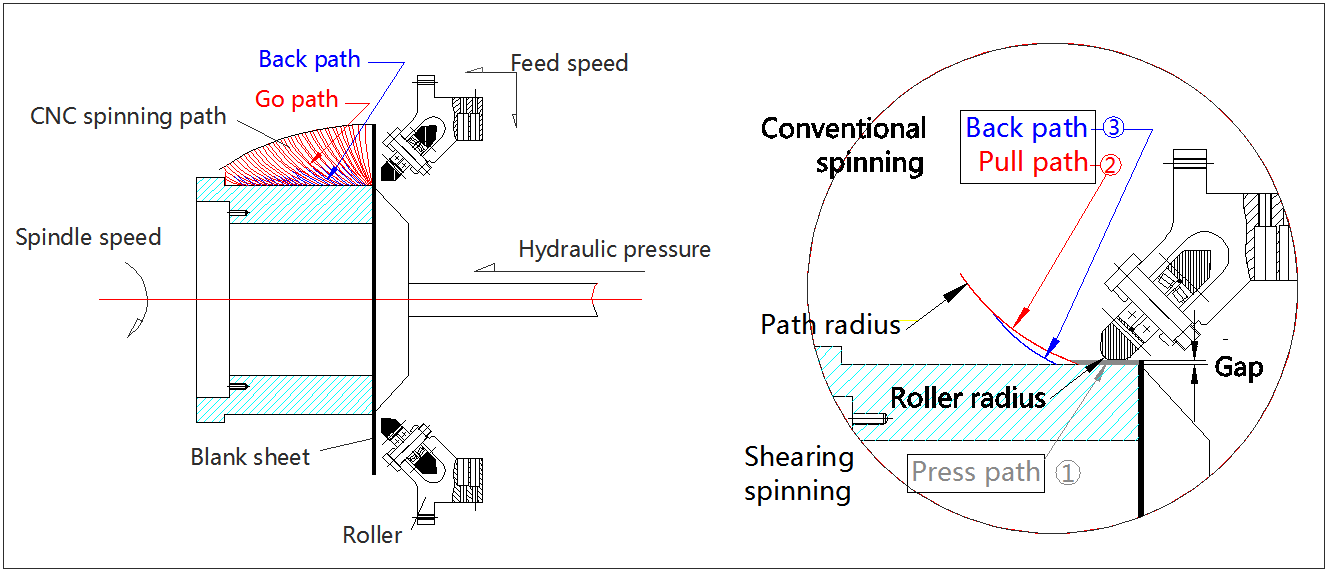
● Spin forming principle
Spinning gradually shapes the workpiece along the predetermined forming route through the knife wheel. During the forming process, the material is subjected to the pulling and pressing of the knife wheel. Pulling causes the blank to become longer and thinner, while pressing causes the blank to become longer and thinner.
All of the spinning path is divided into small units, with a total of 3 steps. ① Press path - ② Pull path - ③ Back path
① Press path (gray color): to make the workpiece hold the mold tightly.
② Pull path (red color) : Gradually deform the shape of the workpiece towards the mold.
③ Back path (blue color) : to make workpiece hold the mold tightly, Avoid the unidirectional pull path caused by the floating to prevent the local area from thinning and breaking too quickly.
● Spinning forming helical line
At each step of the spinning forming tool wheel movement, the relative motion trajectory between the workpiece and the tool wheel is a helical line. The movement trajectory of the helical line is mainly determined by the radius of the tool wheel, the radius of the tool path, the spindle speed and the feed rate.
① Spindle speed
The spindle speed is higher, the pitch distance of the helix is shorter, the length of the helix in contact between the roller and the workpiece is longer, and the workpiece is stretched by roller longer. If the workpiece is drawn deep and thinned, it will crack.
② Feed speed
The feed speed is slower, the pitch distance of the helix is shorter, the length of the helix in contact between the roller and the workpiece is longer, and the workpiece is stretched by roller longer. If the workpiece is drawn deep and thinned, it will crack.
● Pulling force
The pulling force of spin forming is related to the roller radius and path radius. The roller and path radius is big, the pulling force is less, the workpiece thinning is less.
● The limit of materials
There are three reasons for workpiece cracking. The first is excessive stretching (pull path) to the limit of the blank's elongation rate, which leads to cracking. The second is that excessive shearing and extrusion (press path) cause the workpiece to be sheared and broken. The third is that the repeated bending (pull path) of the workpiece causes it to reach the fatigue limit and break.
CNC metal spinning path and parameter>
8. CNC programming
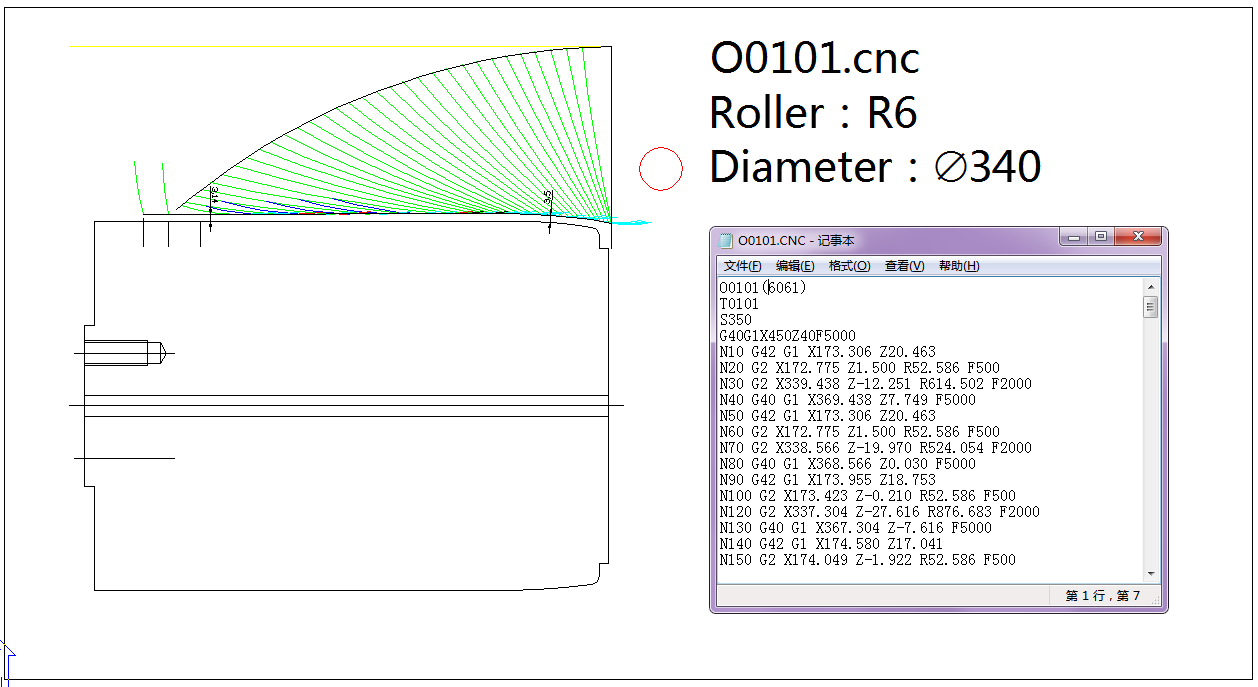
Nowadays, many CNC machine tool manufacturers come with software for automatic production programs, which saves a lot of programming time. You just need to open the drawn tool path diagram with the software, and the program can be generated. However, it is still best to memorize the basic program instructions to facilitate further adjustment, optimization and modification of the program.
G00 : Rapid positioning. The tool moves to the specified position at the machine's maximum speed without cutting.
G01 : Linear interpolation. The tool cuts along a straight path at the set feed rate.
G02 : Clockwise circular interpolation. The tool cuts along a clockwise circular arc.
G03 : Counterclockwise circular interpolation. The tool cuts along a counterclockwise circular arc.
G40 : Cancel tool radius compensation. Turns off the tool radius compensation function.
G41 : Left tool radius compensation. The tool compensates along the left side of the workpiece contour (viewed along the feed direction).
G42 : Right tool radius compensation. The tool compensates along the right side of the workpiece contour (viewed along the feed direction).
M03 : the main shaft rotates forward. Start the main shaft, usually by rotating it clockwise.
M04 : spindle reversal. Start the main shaft, usually by rotating counterclockwise.
M05 : spindle stops. Stop the main shaft from rotating.
S : Spindle speed
F : Feed speed
This is the spinning roller path diagram and program of the spinning finished product, which can be downloaded for study>
9. Parameter setting
The parameter Settings of numerical control spinning include spindle speed, feed rate, X-axis tool compensation, Z-axis tool compensation, and roller radius.
● Roller radius
The size of the radius can be detected during input using the Radius gauge. Input the actual radius value of the roller.
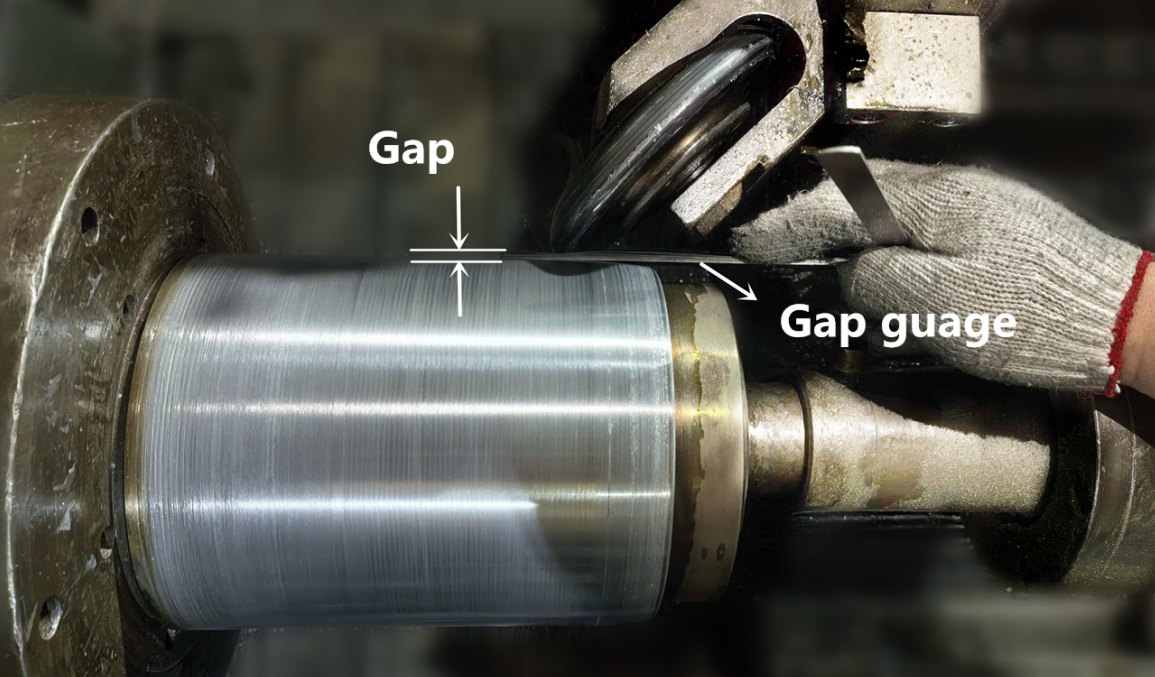
● Gap ( X-axis and Z-axis compensation)
The gap value refers to the gap value maintained between the cutter wheel and the die during the final shearing and spinning process. This gap value can be controlled through the gap compensation of the X-axis and Z-axis. The setting of the gap value is mainly related to the thickness of the spun material, the type of material, the thinning rate, and the magnitude of the machine's output spinning force. The harder the material, the thinner the coarse blank for spinning, the smaller the machine's spinning force, and the smaller the set gap value.
Generally, the initial value of the gap is set a bit larger, to avoid damage to the spinning machine caused by overly tight clearance. After testing and forming a product and remove the work piece from mandrel, the correct gap value is determined by observing the external and internal surfaces of the workpiece. If the internal surface of the workpiece is not smooth, it indicates that the gap value is too large. If the spinning marks on the external surface are uneven and suddenly show oblique marks, it indicates that the local gap value is too small.
There is a more convenient method. When the formed workpiece is placed on the mold, use a steel bar with a diameter of approximately 12mm to strike different positions of the workpiece. If the sound is very clear, it indicates that there is a gap between this part and the mold, and the originally set gap value is too large. If the sound is very small, it indicates that the gap here is already appropriate.
● Spindle speed and feed speed
|
Material |
Diameter |
Spindle speed |
Feed speed - pull path |
Feed speed- Press path |
|
Aluminum Or copper |
150mm |
1800rpm |
6000mm/min |
500mm/min |
|
300mm |
1000rpm |
3000mm/min |
300mm/min |
|
|
500mm |
600rpm |
1500mm/min |
200mm/min |
|
|
1000mm |
400rpm |
800mm/min |
100mm/min |
|
|
Mild Steel |
150mm |
1200rpm |
5000mm/min | 450mm/min |
|
300mm |
800rpm |
2000mm/min | 350mm/min | |
|
500mm |
500rpm |
1000mm/min | 300mm/min | |
|
1000mm |
300rpm |
500mm/min | 100mm/min | |
|
Stainless steel |
150mm |
1000rpm |
3000mm/min |
350mm/min |
|
300mm |
600rpm |
1500mm/min |
300mm/min |
|
|
500mm |
400rpm |
800mm/min |
200mm/min |
|
|
1000mm |
200rpm |
400mm/min |
100mm/min |
The thickness of the material is thicker, the hardness and tensile strength is higher, the spun product diameter is bigger, you can choose the slower the spindle and feed speed.
10. Mold and roller installation
● Requirement
The mold installation needs to control the entire outer circle runout within 0.03mm, and the outer circle runout of the tool wheel installation needs to be controlled within 0.02mm.
● Runout influence
The runout between the roller and the mold will make the gap unstable. The thickness of the final spun product will be uneven in any cross-section. Excessive runout will lead to the local roller pressing the workpiece too tightly, resulting in cracking.
11. Clamping
● Runout
When the clamping rotates together with the mold, it should not cause too much jumping. Otherwise, the pressure exerted by the clamping on the material sheet will be uneven, making the bottom of the product prone to scratches or the material sheet may not be able to hold up and be thrown out in the spinning.
● Pressure adjustment
The pressure at the tail hydraulic cylinder should not be adjusted too high. Generally, the initial value can be set to 0.4MPa. The larger the diameter and thickness of the spun product, the greater the pressure at the tail cylinder required. Additionally, the smaller the area at the bottom of the spun product, the greater the pressure at the tail cylinder needed. However, the pressure value of the tail cylinder is too high. Excessive pressure can lead to a reduction in the service life of the tail top bearing.
12. CNC program running test
When all the above work is ready, you can start running and simulating the program. When simulating the program, the command for the spindle to rotate M03 or M04 can be deleted, the feed ratio can be reduced, and the movement trajectory of the spinning tool wheel can be simulated separately when the spindle does not rotate. There are three functions of simulation. At first, it checks whether there is any interference between the entire knife movement and the machine. Second, when there is an error in the program, it can cause roller collision accident. Third, it is necessary to measure the gap value between the roller and the mold during shearing spinning.
13. Sample testing
After the program simulation is completed and confirmed to be not problem, the M03 command of the program can be added, and the metal sheet can be placed for spin forming.
14. Problem adjustment
● Gap adjustment
The gap affects the thickness of the spun product, as well as the internal and external appearance effects. For specific adjustments, please refer to the parameter setting methods mentioned above in the article.
● Spindle speed and feed speed
The speed of the spindle and feed affects the thinning rate of the material when it is pulled during conventional spinning (go path and back path). The faster the spindle speed, the slower the feed speed, and the thinner the thickness of the raw material will be pulled by the spinning tool wheel.
● Spin forming path
The main problems in spinning during forming are wrinkling and cracking.
The reason for wrinkling is that the strength at the position of the maximum diameter of the workpiece is not enough. The radius of the tool wheel and the radius of the tool path can be relatively reduced.
The cracking is due to local thinning caused by multiple stretching. It can be formed by using back path, or by increasing the roller radius and path radius. Additionally, checking whether the workpiece is tightly attached to the mold, you can reduce the gap by adjusting press path if the workpiece have gap with mold.
15. Process record
When the sample is successfully debugged, the following process documents need to be well recorded.
● Spin forming path drawing
● CNC programming
● The gap compensation values of the X-axis and Z-axis
16. Hot spinning
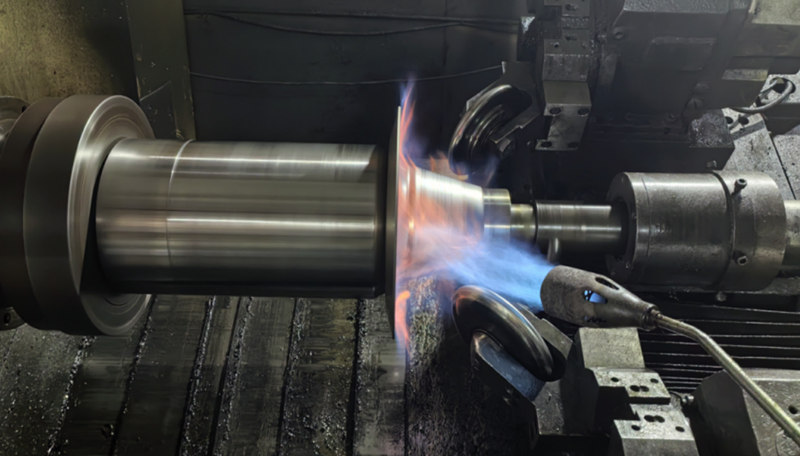

When the hardness and tensile strength of the metal is higher than 304, the thickness is over 2.5mm, it needs more spinning force, in order to reduce the wear of the machine, it can use hot spinning.
17. Tube spinning
Compared with sheet spinning, the spinning path for tube spinning is much simpler. The main factor related to tube spinning is the design of the tube spinning fixture. As long as the tube does not move during the spinning process, it can be formed easily.
Recommended
- -Spin forming principle-CNC metal spinning technology
2026-02-22 - -What is CNC metal spinning machine tool
2024-08-15 - -Aerospace components-Precision manufacturing of CNC spinning
2025-01-29 - -Metal spun products - what product spin forming can do
2025-01-24 - -How to design a CNC metal spinning mold | mandrel
2024-04-12 - -Metal spinning materials
2024-04-14 - -Metal spinning development and prospect
2024-10-31 - -How to choose a CNC metal spinning machine
2024-04-18 - -Metal spinning process and technology
2024-11-30 - -How to control the accuracy of CNC metal spinning
2024-07-27
